What is Mpox?
Mpox (formerly Monkeypox) is a disease caused by a virus not commonly seen in the United States. However, there is an ongoing, global outbreak and Mpox cases have been found in the United States, including in Nevada.
Mpox virus is related to the virus that causes smallpox, but Mpox is less severe than smallpox and is rarely fatal. Mpox often causes a painful or itchy rash and sometimes causes flu-like symptoms like fever, headache, muscle aches, or other symptoms. Mpox virus is not related to chickenpox.
Anyone can get Mpox. Many of the cases reported during the current outbreak have been among gay, bisexual, or other men who have sex with men. Following the recommended prevention steps can help protect you and your community.
Number of Mpox Cases in Nevada
Mpox case data are summarized in the dashboard link below. Daily new cases are displayed as 14-day moving averages of all cases. Cases per 100,000 are displayed for the most recent 30-day period and cumulatively. In the map below, counties with higher rates are shaded darker.
- Nevada Mpox Dashboard
- Visit your local public health authority’s website to find out about cases in your community:
Symptoms of Mpox
Mpox often causes a characteristic rash. The rash can look like pimples or blisters that appear on the face, inside the mouth, on the hands, feet, chest, genitals, anus or other parts of the body. The rash goes through different stages before healing completely.
Below are a few examples of Mpox rash in different stages:
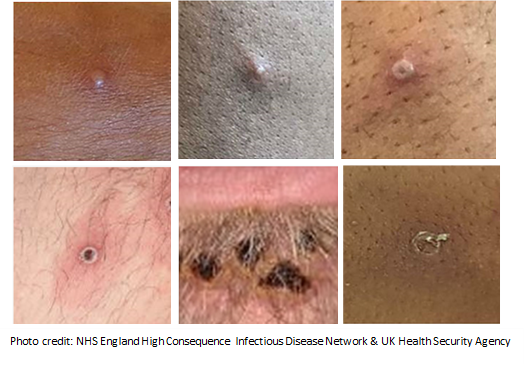
- If you have a rash or other symptoms that concern you, contact a health care provider.
Sometimes Mpox causes other symptoms. Mpox can also cause other symptoms, like fever, headache, muscle aches, back ache, swollen lymph nodes, chills, or exhaustion. Sometimes people get a rash first followed by other symptoms and sometimes people have flu-like symptoms a few days before the rash appears. Others only experience a rash without other symptoms. The illness typically lasts 2-4 weeks.
A person with Mpox is contagious while they have symptoms. Mpox can be spread from the time symptoms start until the rash has healed, which is when all scabs have fallen off and a new layer of skin has formed.
How Mpox Spreads
Mpox spreads in a few ways, as described below.
- During prolonged face-to-face or intimate physical contact with someone who has Mpox.
- Through direct contact with rash, scabs, or body fluids of someone who has Mpox.
- By touching items like clothing, towels, or bedsheets after being touched by rash or body fluids of someone who has Mpox.
- Through the placenta from a pregnant woman who has Mpox to a fetus.
- By being scratched or bitten by an infected animal or by preparing or eating meat or using products from an infected animal.
- Direct exposure to Mpox can happen during intimate contact including:
- Oral, anal, and vaginal sex or touching the genitals (penis, testicles, labia, and vagina) or anus (butthole) of a person with Mpox.
- Hugging, massage, and kissing someone with Mpox.
- Prolonged face-to-face contact with someone with Mpox.
- Touching fabrics and objects that were used by a person with Mpox and that have not been disinfected, such as bedding, towels, fetish gear, and sex toys.
Steps to Prevent the Spread of Mpox
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offer the following three simple measures to prevent spreading Mpox:
- Avoid close, skin-to-skin contact with people who have a rash that looks like Mpox.
- Avoid contact with objects and materials that a person with Mpox has used.
- Wash your hands often.
If you have been diagnosed with (or think you might have) Mpox
- Contact a health care provider or your local health department if you do not have a health care provider.
- Southern Nevada Health District (Clark County)
- 702-759-1300 (24 hours)
- Washoe County Health District
- 775-328-2447 (24 hours)
- Carson City Health and Human Services (Carson City, Douglas, and Lyon counties)
- 775-887-2190 (24 hours)
- Nevada Division of Public and Behavioral Health (all other NV counties)
- 775-684-4200 (M to F 8 am to 5 pm) or 775-684-5920 (after hours)
- Central Nevada Health District (Churchill)
- 775-867-8181
- Take care of yourself and others
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA)
If you think you have been exposed to Mpox but do not have symptoms, it is still important to contact your health care provider or local health authority (see the information listed above)!
Additional Mpox Resources

